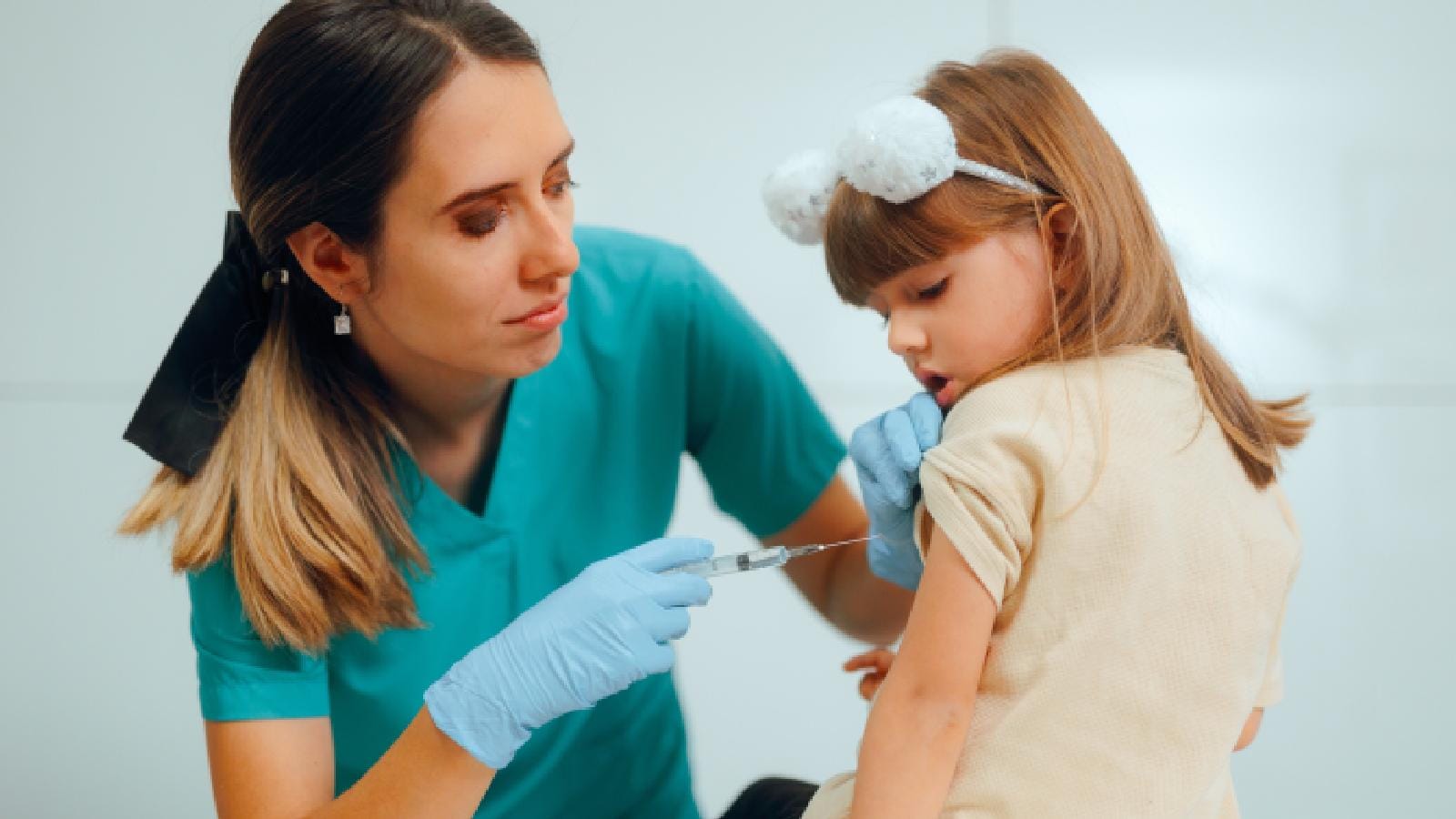
Tetanus vaccine can provide protection against the bacterial infection known as tetanus. But does everyone need the jab or is it just for children? On National Vaccination Day, we tell you whether adults also need this shot or not.
Getting cuts while cooking or gardening is pretty common, so you may not give it much thought. But if it involves a rusty object, you may think about the tetanus vaccine. Yes, it is the same shot that’s given to children, who need several doses at different ages. It is a way of protecting you and your child from tetanus, which is a life-threatening bacterial infection. You can get tetanus if the soil near your house or workplace containing bacteria gets into a wound such as a burn or cut. But if you got the shot during childhood, do you still need it? On the occasion of National Vaccination Day, which is observed on March 16 in India, we tell you all about it.
What is the tetanus vaccine?
It is a vaccine that protects against tetanus, a bacterial infection that is caused by Clostridium tetani. “This bacteria produces a toxin that negatively impacts the nervous system. It leads to muscle stiffness and spasms, especially in the jaw and neck, and can make it difficult to breathe,” says physician and infectious disease specialist Dr Tharanath S. The infection spreads through open wounds, cuts, burns, or animal bites when they come into contact with contaminated soil, dust, or rusted objects.
“Since the bacteria exist widely in the environment, getting a jab is the only way to prevent infection. The tetanus vaccine helps the immune system develop antibodies to neutralise the tetanus toxin and prevent severe illness and even death,” says the expert. There are different types of tetanus vaccines, which provide protection against other diseases too, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention:
- DTaP: Diphtheria, tetanus, and whooping cough or pertussis
- Tdap: Tetanus, diphtheria, and whooping cough
- Td: Tetanus and diphtheria

Who needs the tetanus vaccine?
Tetanus is rare, but the chances of getting it are higher if you have a big or deep wound or it is very dirty, as per the UK’s National Health Service. “So, the tetanus vaccine is necessary for almost everyone. Tetanus bacteria exist in soil, dust, and animal waste, making infection possible through even minor wounds,” says the expert.
- Children receive the vaccine as part of their routine immunization. Babies receive their first dose at 6 weeks as part of the DTaP vaccine. “This is followed by additional doses at 10 weeks, 14 weeks, 15 to 18 months, and a final dose between four and six years,” shares Dr Tharanath.
- Adolescents should receive a Tdap booster when they turn 11 or 12.
- Grownups need a Td booster every ten years to maintain immunity. Adults who were never vaccinated or who didn’t get all the shots as a child should receive a Tdap jab followed by the Td booster dose 10 years later, according to the CDC.
- Pregnant women should receive a Tdap vaccine during each pregnancy to protect their newborn from neonatal tetanus.
- People who suffer from deep or contaminated wounds may need a booster shot if their last dose was given more than five years ago.
- Even those who have had tetanus before still need the vaccine because natural infection does not provide long-term immunity.
“Staying updated with tetanus boosters is the only reliable way to prevent this serious and potentially fatal disease,” says the expert.
Who does not need the tetanus vaccine?
While almost everyone benefits from the tetanus vaccine, there are a few exceptions.
- Infants younger than six weeks old are not given tetanus vaccine, as their immune systems are not fully developed to respond to it.
- People who have had a severe allergic reaction to a previous tetanus vaccine should avoid further doses unless given a green signal by a doctor.
- People with severe immunosuppressive conditions, such as undergoing chemotherapy for cancer, may require a modified vaccination strategy.
“However, since tetanus is a life-threatening disease and there is no natural immunity, nearly everyone should receive the vaccine at some point in their life,” says the expert.
How long does the tetanus vaccine last?
The protection from a tetanus vaccine typically lasts for about 10 years, after which immunity gradually declines. To ensure you get protection for long, a booster dose of Td or Tdap is required every 10 years. “However, in cases of serious wounds, such as deep cuts, burns, or animal bites, a booster may be required earlier if the last dose was given more than five years ago,” says the expert.

What are the side effects of the tetanus vaccine?
The tetanus vaccine is generally well tolerated by people, including children, with most side effects being mild and temporary.
- The most common reaction is pain, redness, or a little bit of swelling at the spot where you got injected.
- Some may experience mild fever, fatigue, headache, or muscle soreness.
- Few people may develop mild nausea or feel unwell for a short period after getting the jab.
“But these symptoms don’t last for a long time and go away on their own,” says the expert.
“Serious side effects of this vaccine are extremely rare, but can include severe allergic reactions such as difficulty breathing, rash or swollen face,” says the expert. If these occur, immediately check with a doctor.
Tetanus vaccine is a must for children as well as adults. It can offer protection from tetanus, which is a serious bacterial infection.
Related FAQs
Can women be given tetanus vaccine during pregnancy?
Yes, the tetanus vaccine is safe and highly recommended during pregnancy to protect both the mother and baby. Pregnant women receive the Tdap vaccine, which provides immunity against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis. It is ideally given between 27 and 36 weeks of pregnancy, as this allows the mother to develop antibodies that are passed to the baby, offering protection in the first few months of life.
When to get a tetanus shot after a cut?
A tetanus shot should be considered if you suffer a deep cut, especially if the injury involves rusted objects. If you have received a tetanus vaccine within the last five years, an additional booster is usually not needed. However, if your last dose was more than five years ago, or if you are unsure about your vaccination history, getting a booster is recommended.
#Tetanus #vaccine